ES6 +¶
- Modernized JavaScript for large-scale apps.
- ES evolution
- JS revision(Github)
class/Object¶
- Set default values for function parameters
- function greet(name = "Guest") {... }
- short hand for object lietrals:
- const obj = { name, greet() { /_ ... _/ } };
- class (Syntactic sugar over prototypes)
-
Datatype:
-
const id = Symbol("id"); // new datatype
-
BigInt
-
Object.values()/Object.entries()
- Object.fromEntries([['a', 1]]); // { a: 1 }
1. CONST¶
- immutable property
2. LET¶
- same as var but with block scope
- unlike var cannot use let before declaration
- block means --> if-block, for-block, normal-block - just { }
- With ES6 modules and block-scoped variables (let/const), some IIFE use cases are less common today.
IIFE¶
- IIFE (Immediately Invoked Function Expression)
- JavaScript function that runs as soon as it's defined
- powerful pattern with several important use cases.
- key features
- Creates a new scope for variables
- Variables inside aren't added to the global scope
(function() {
// Code here runs immediately
console.log('IIFE executed');
})();
(function() {
// Code here
}());
(async function() {
const data = await fetch('https://api.example.com');
console.log(data);
})();
3. String¶
- Template Literals : console.log(
Hello, ${name}!); - new methods : s.startswith(),endswith(),includes(), etc
- padStart()/padEnd()
4. Collection¶
- [1, 2, 3].at(-1); //negative index
- Map & Set
- Array.from(), Array.of(), find(), findIndex(), includes(), findIndex()
- Array.flat , flatMap
array1.findIndex( (e) => {} )
array1.find( (e) => {} )
[1, 2, 3].findLast(x => x < 3); // 2
[1, 2, 3,3,3].findLastIndex(x => x < 3) //4
5. For loop¶
- Better way to iterate.
let e of array1 const e of array1 for await (const item of asyncIterable) { ... }
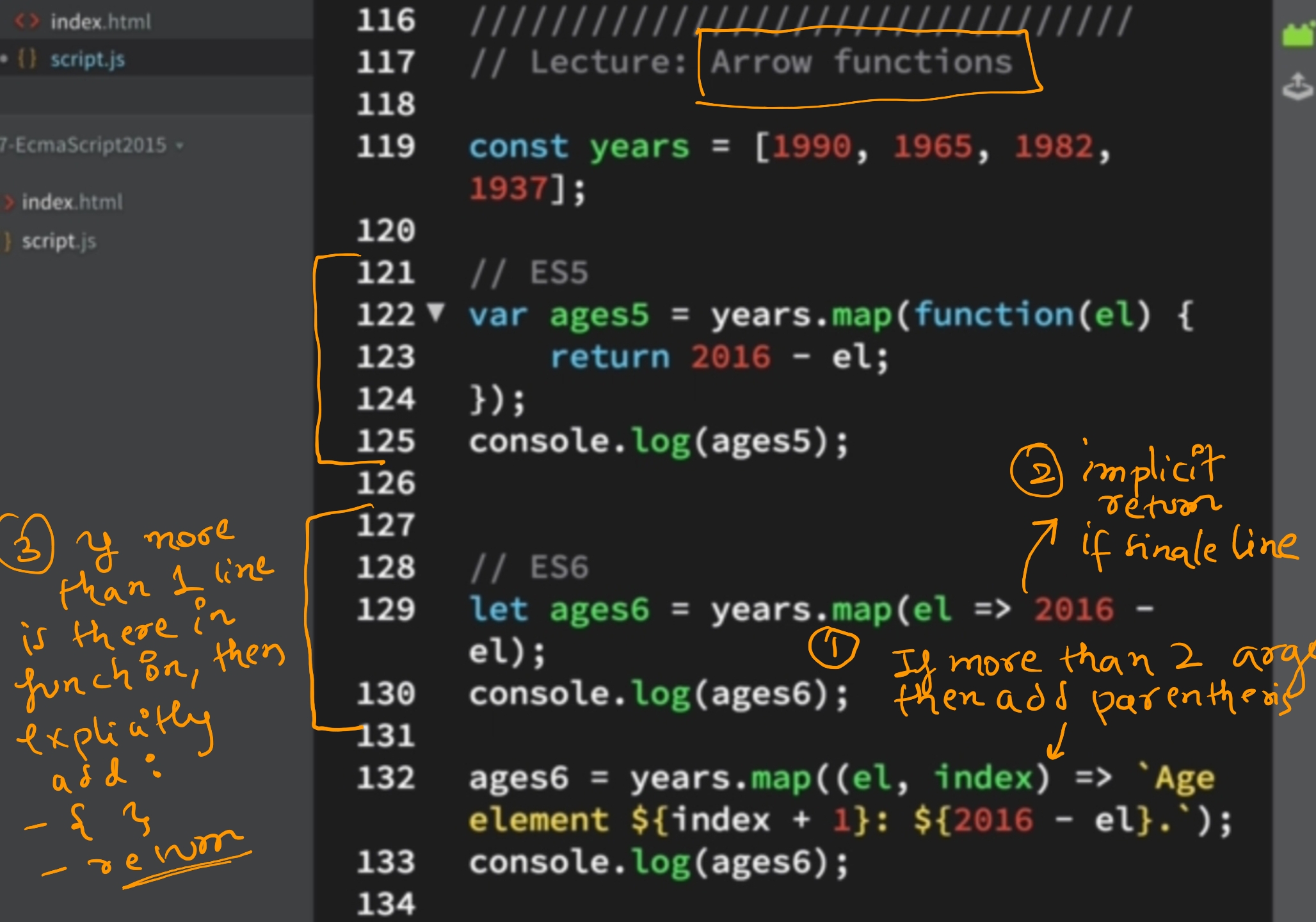
6. Arrow Function¶
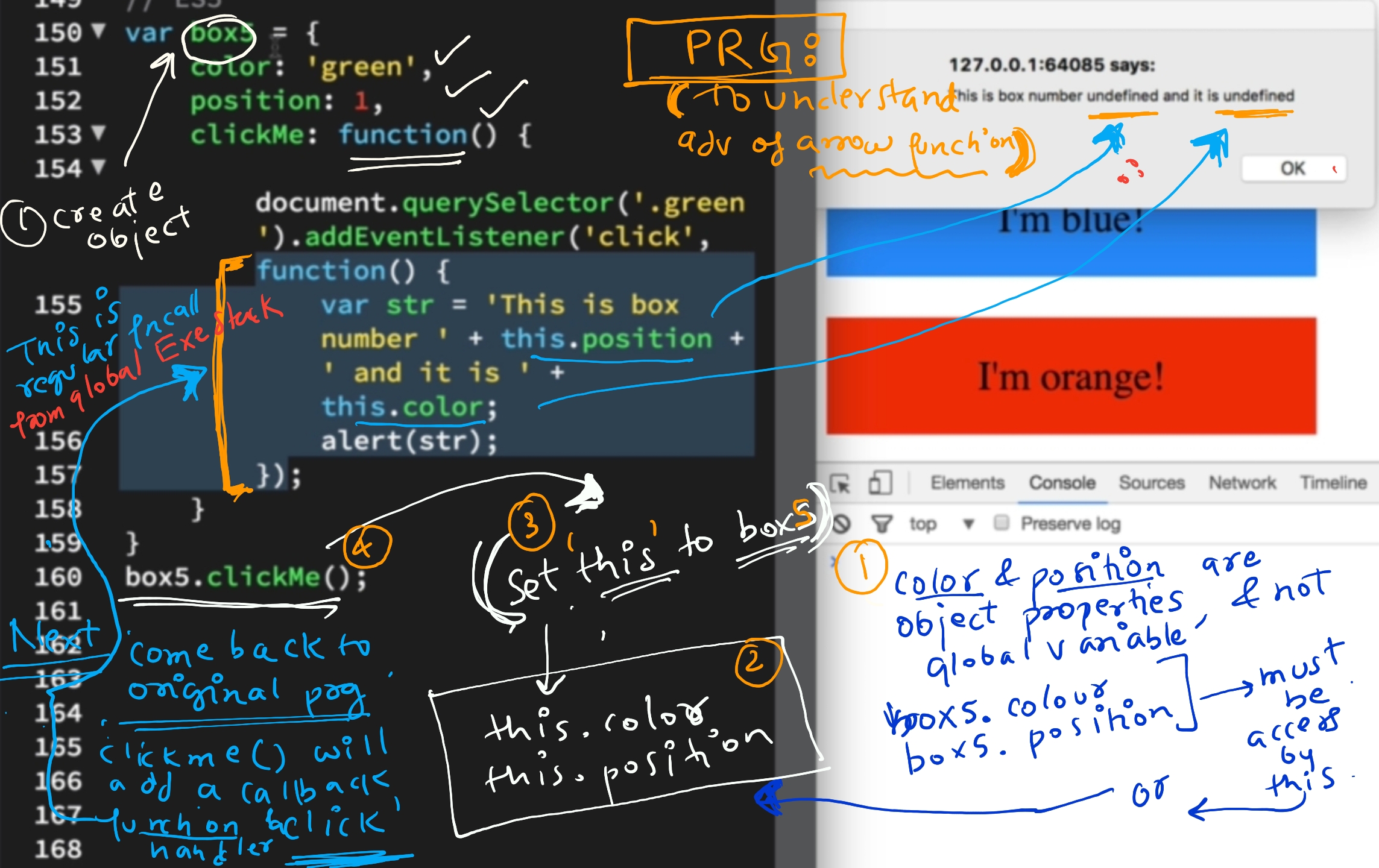
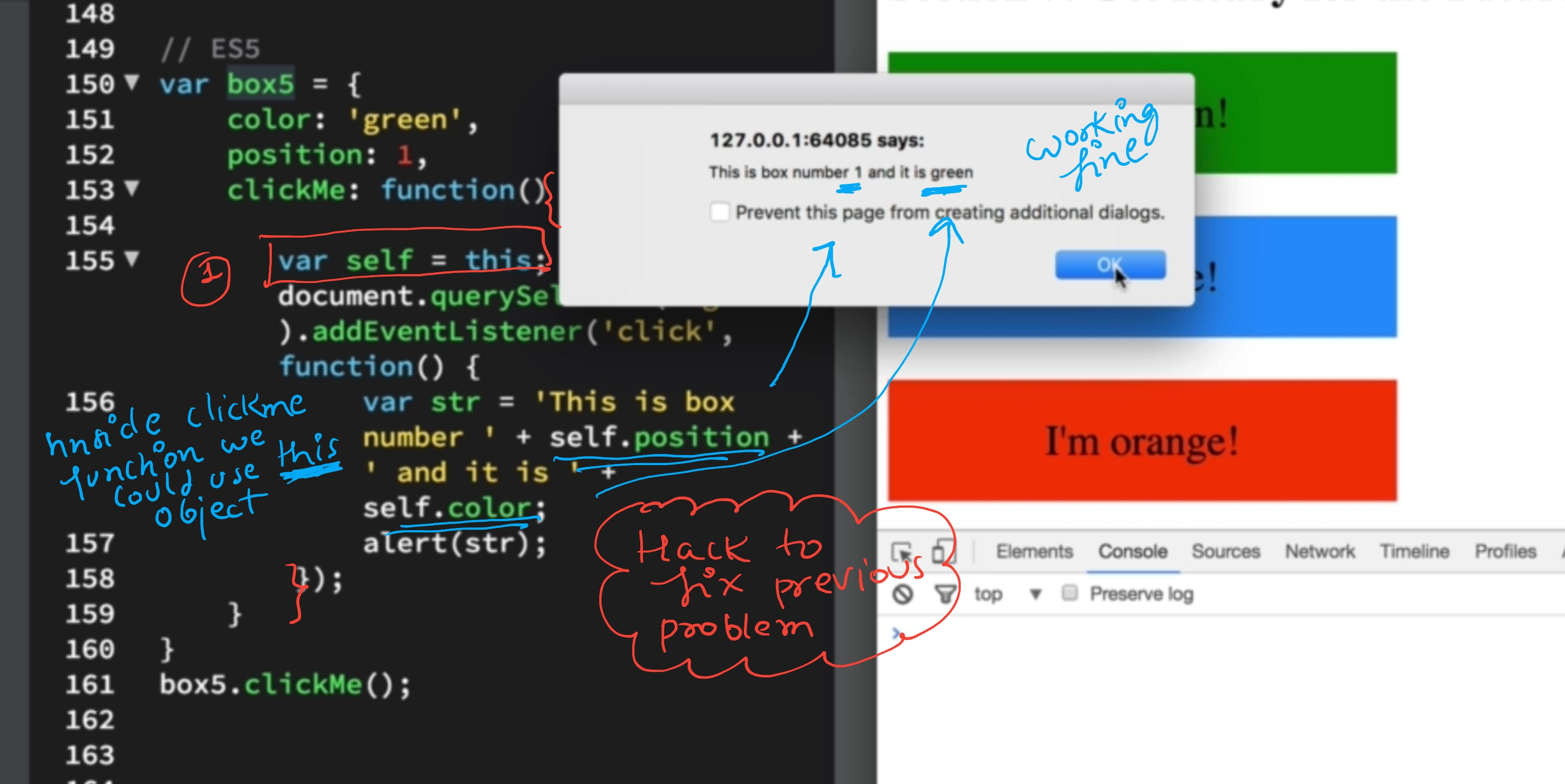
- Cannot Be Used as Constructors fn
- Unaffected by call, apply, bind
- implicit return
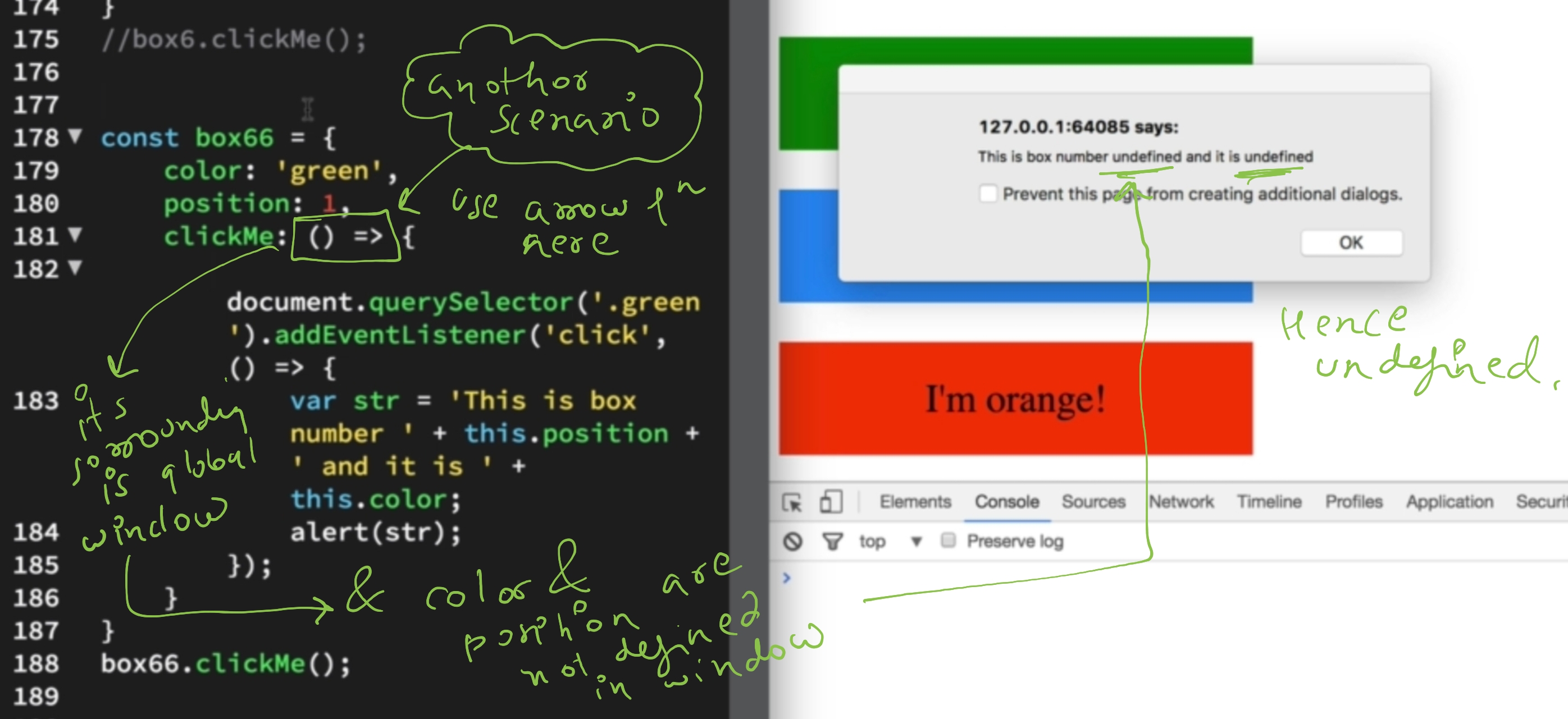
- have their own
this- they lexically capture the this value from their surrounding context
=== this ===
const obj = {
value: 'Hello',
arrowFunc: () => {
console.log(this.value); // `undefined` (inherits from outer scope)
}
};
obj.arrowFunc();
const obj = {
values: [1, 2, 3],
print: function() {
this.values.forEach(() => {
console.log(this); // `obj` (inherited from print's `this`)
});
}
};
obj.print();
- Use regular functions when:
- You need method functions that access the object via this.
- You need constructor functions
- You want dynamic this binding
-
Use arrow functions when:
-
You need to preserve the lexical
this(event handlers, callbacks) - You want concise syntax for simple functions
- working with functional programming patterns
7. Spread & Rest Operators¶
- const arr = [1, 2, ...[3, 4]] // Spread: Expand arrays/objects. eg:
- combine 2 arrays
- function sum(a1, a2, ...nums) // Rest: Collect remaining arguments
- var args
- must be last arg
- const merged = { ...obj1, ...obj2 };
8. Modules (import/export)¶
- export const pi = 3.14; // Export
- import { pi } from './math.js'; // Import
- dynamic import : Load modules only when needed
button.addEventListener('click', async () => {
const utils = await import('./utils.js');
utils.doSomething();
});
if (user.isAdmin) {
const adminModule = await import('./admin.js');
}
--ReactJs
const LazyComponent = React.lazy(() => import('./LazyComponent'));
9. Promises¶
- fetch(url)
.then(response => response.json())
.catch(error => console.error(error));
- Promise > finally ( cb )
- Promise.all, allSettled, allresolved, any, race
- asysnc/await
10. more¶
-
!/usr/bin/env node // Shebang syntax for Node.js scripts:¶
- try { ... } catch { /_ no parameter needed _/ }
- const value = input ?? 'default'; // Fallback for null/undefined:
- const name = user?.profile?.name;
- Dynamic Imports (import())
- globalThis : Unified way to access the global object (window, global, etc.).
- const billion = 1_000_000_000; // Improves readability
- throw new Error('Failed', { cause: originalError });
- 2 ** 3; // 8 (instead of Math.pow(2, 3))
Screenshots(Extra)¶