Promise
Promise¶
A. feature:¶
- Object that keeps track that whether a certain
eventhas completed or not.
event means - DOM event, async call made to server to load data, etc
- Once event is complete (eg: asyn call complete to fetch data from backend), it determines what to do after event complete.
- it implements the concept of
future state, to store the returned data.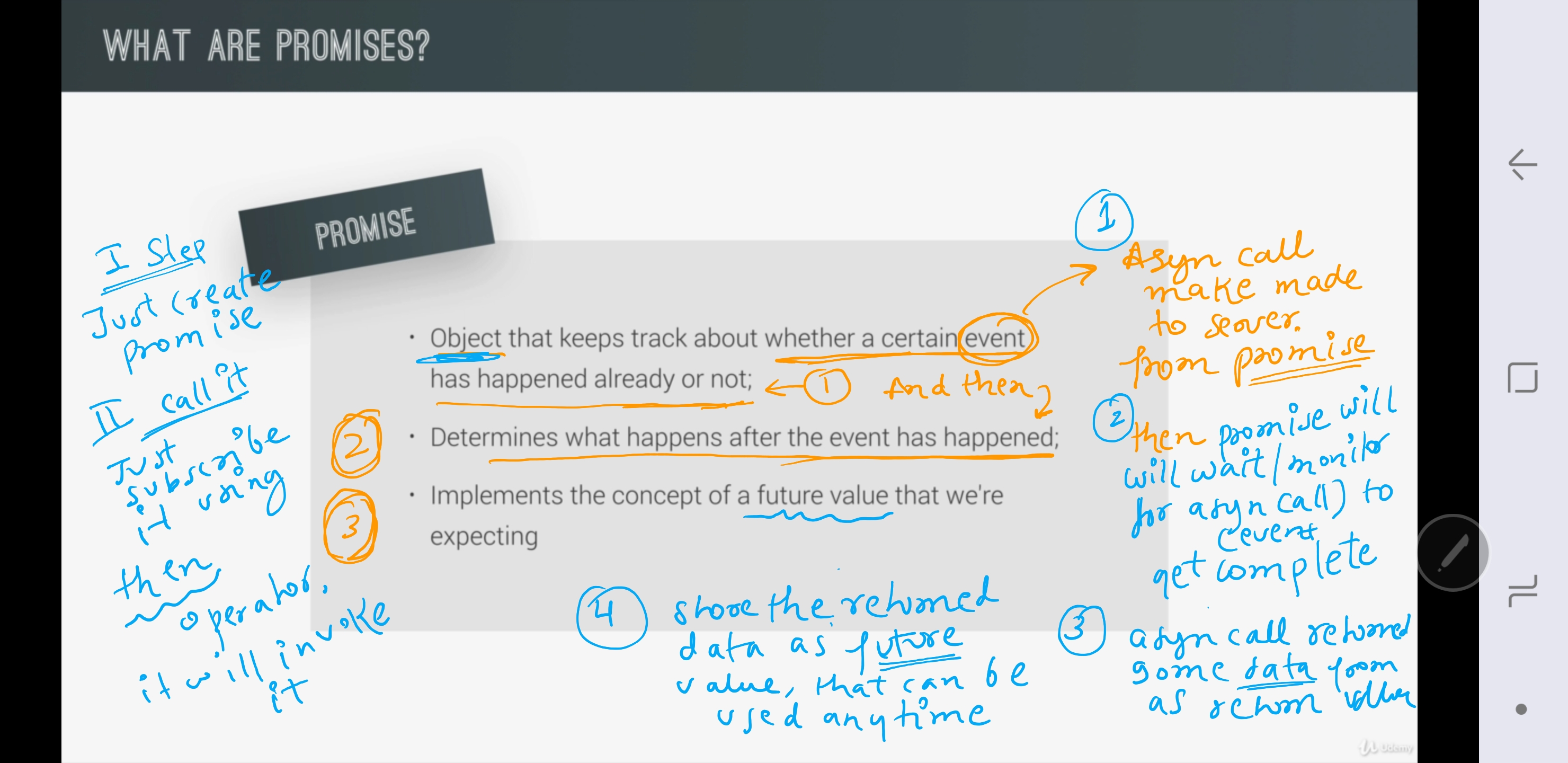
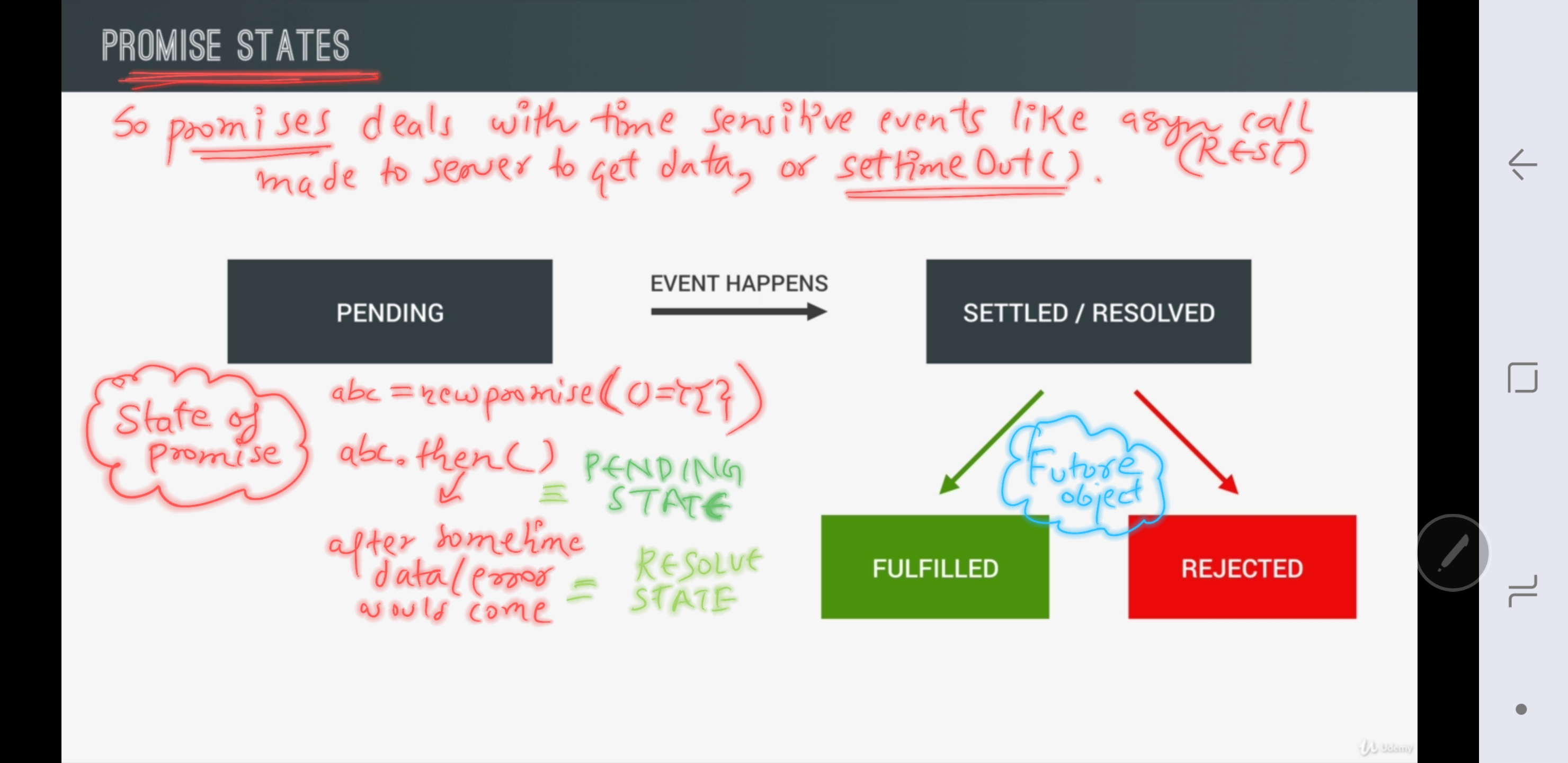
Promise State:¶
Pending and fulfilled/rejected
Create and consume Promise:¶
- create:
const promise1 = new Promise(
(resolve, reject) => {
resolve(data1)
//reject(error1)
});
- it accept callback function which further receive 2 callback function - resolve and reject.
- resolve will send data
-
reject will send error-data or message.
-
consume:
promise1
.then(data1 => {}).then
.catch(error1 => {});
- CAll promise chain
promise1
.then(data-p1 => { return promise2}).then(data-p2 => { return promise 3}).then( ... so on)
.catch(error1 => {});
- data1 and error1

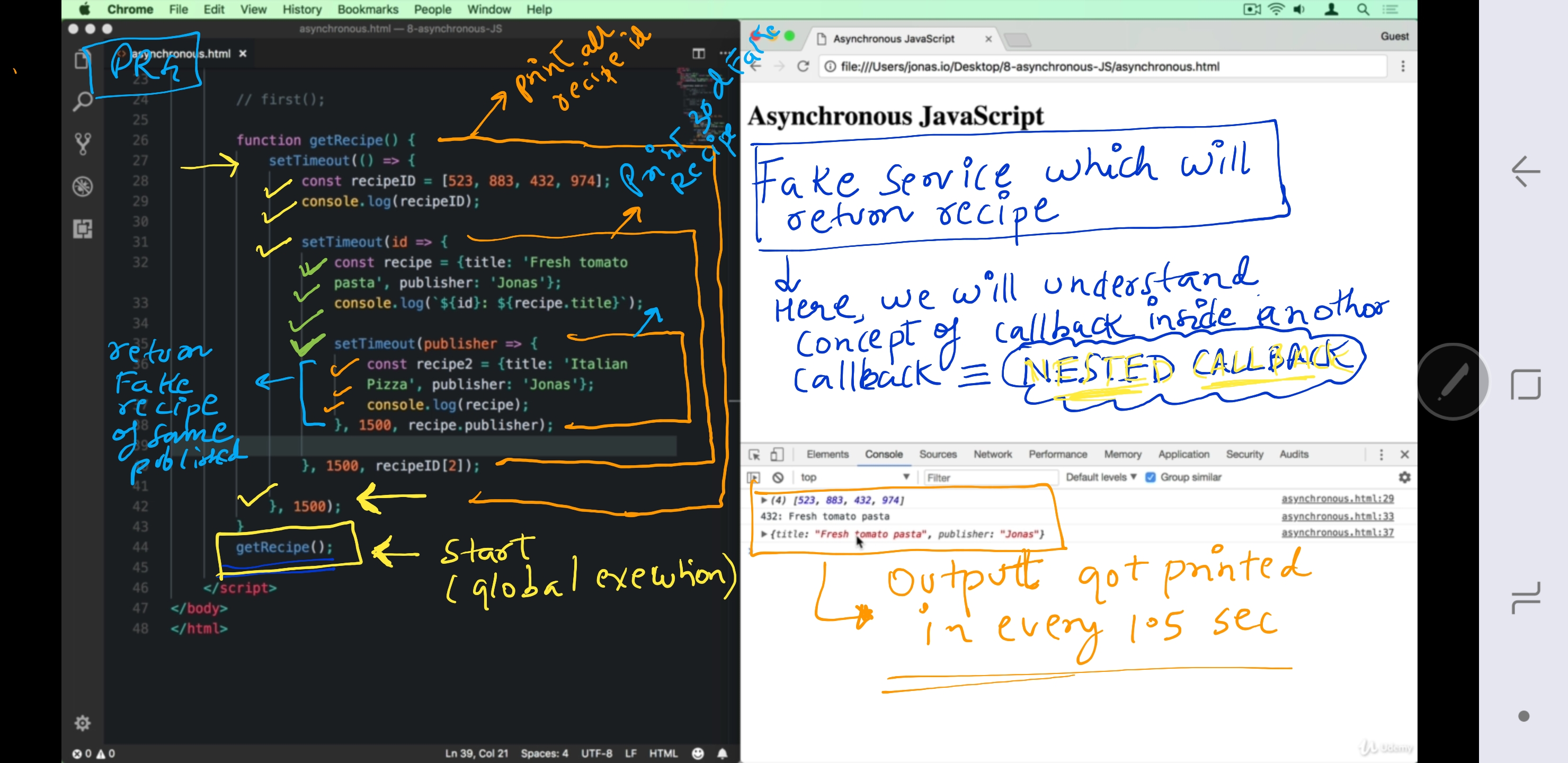
PRG-1 : Nested callback : CALLBACK HELL¶
prgram to understand the need of promise.
- creating fake service with
setTimeOut() - Service name - getRecipe > callback1.
note: callback method is setTimeOut is create fake service. in real invoke AJAX call to make REST call(http-client, httl-request, axios, fetch)
-
callback1: Get all recipeID + Callback2 -
callback2: fetch recipe object for recipeid-2 + callback3 -
passing recipeid-2 as input to callback2. see line 40.
-
callback3: fetch another recipe with same publisher (as that of recipe-2) > finally return it. -
passing recipe2's publisher as input to callback3. see line 38.
all callback(asyn call) will run in parallel.
prblem of callback hell¶
- messy code, difficult to understand data being passed and returned from nested callback.
- if would have more deeper chain, then...
Better way to write PRG-1¶
- use ES6 feature
Promises - see PRG-2
PRG-2: Prmise variant of PRG-1¶
- With promise we dont need to write nested callback chain.
- just write isolated promise for each callback chain. (see prg img below)
-
subscribe(consume) to promise and chain there output using then operator.
-
flow:
-
Define promise1, 2 and 3.
callback1 --> promise1, callback2 --> promise2, etc
- subscribe to callback1 using then( fetch promise1 data, return promise 2 )
- chain then (fetch promise2 data, return promise 3)
-
chain then (fetch promise3 data)
-
prg img1 - p1 and p2
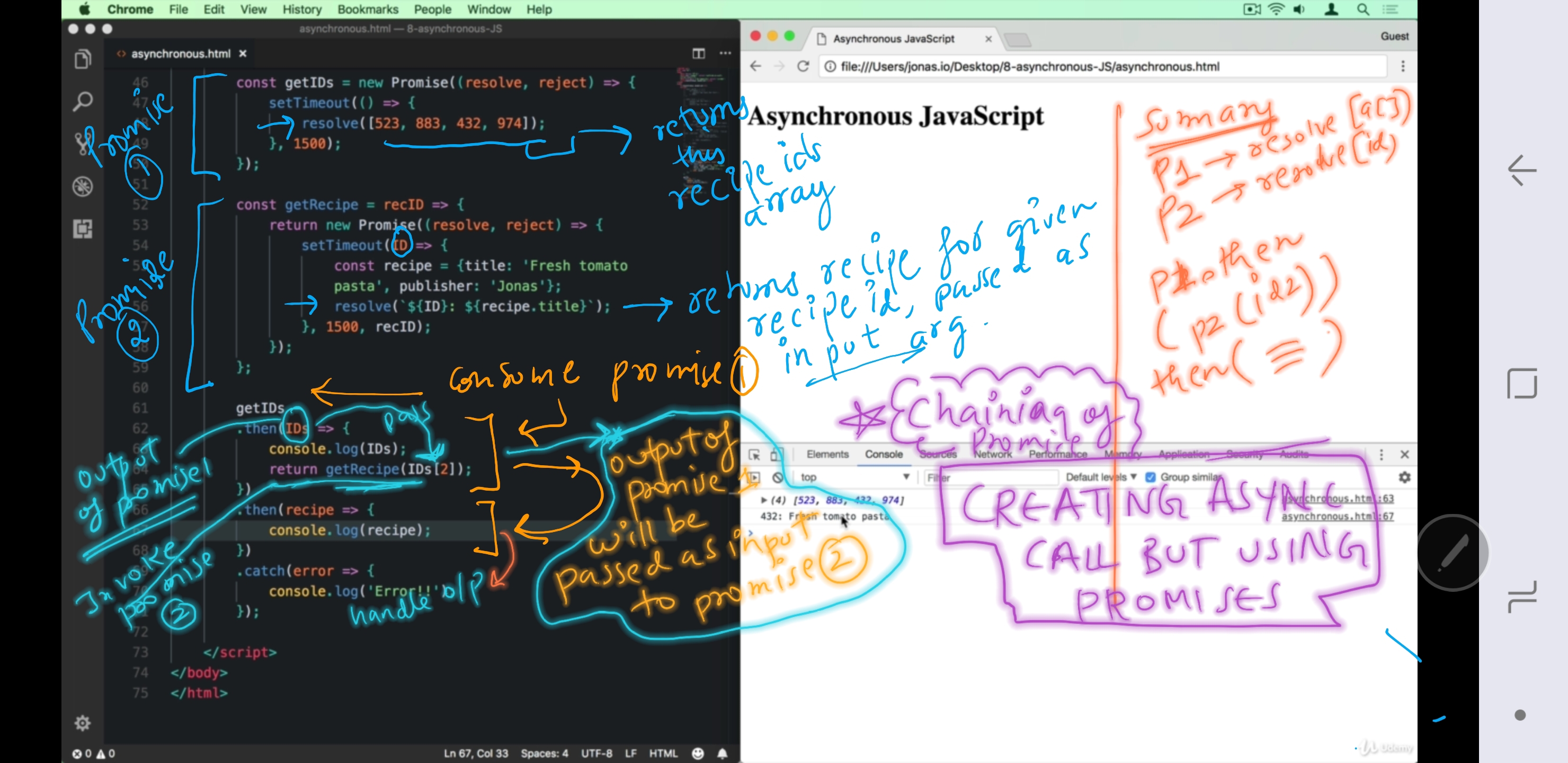
- prg img2 - p3

problem¶
- lot of then statement.
Better way to write PRG-1¶
- use ES7 feature -
Asyncandawait - see PRG-3
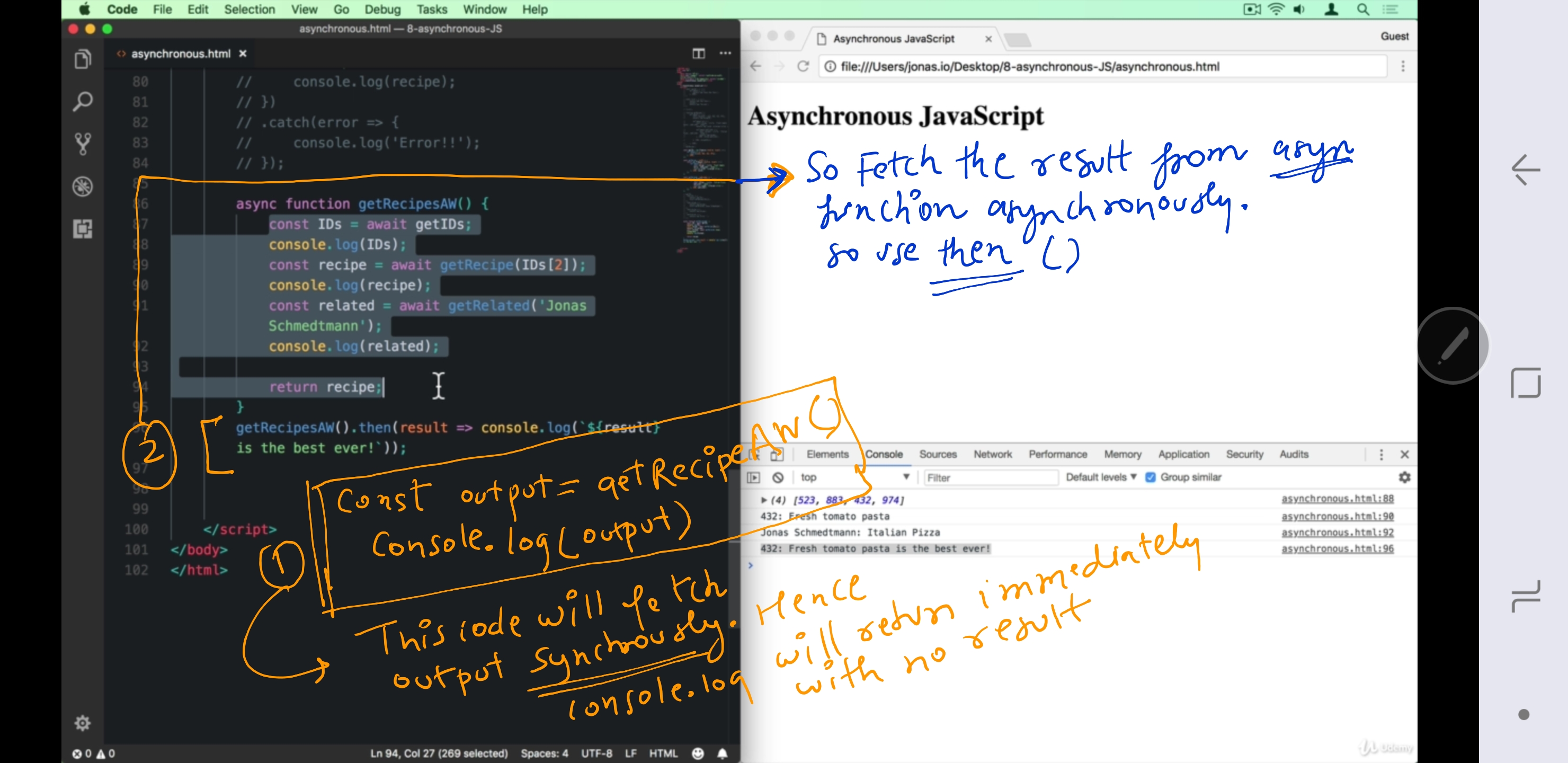
PRG-3: more Better approach to consume promise.¶
- just write
asyncfunction - inside it invoke promise with await keyword.
- Call
asyncfunction, it will run asynchronously, it will be go execution stack and all. - await keyword hold the execution of
async function f1(){
// use await keyword inside asyn function only
}

- subscribe to asyn function to get result asynchronously.