Data Types & Fundamentals
1. JS intro¶
- functional | lightweight | precompiled | scripting language for browser.
- online playground: https://jsbin.com/
- pollyfills
- run on Server by Node.js
- Hoisting - JS declares the variable and method inside Excecution stack before excution.
- if var is not used, then it will be always global, irrespective wherver variable is defined.
- scope - local | global | block
- if (null == undefined) // true - both have internally same value.
2. JS engine¶
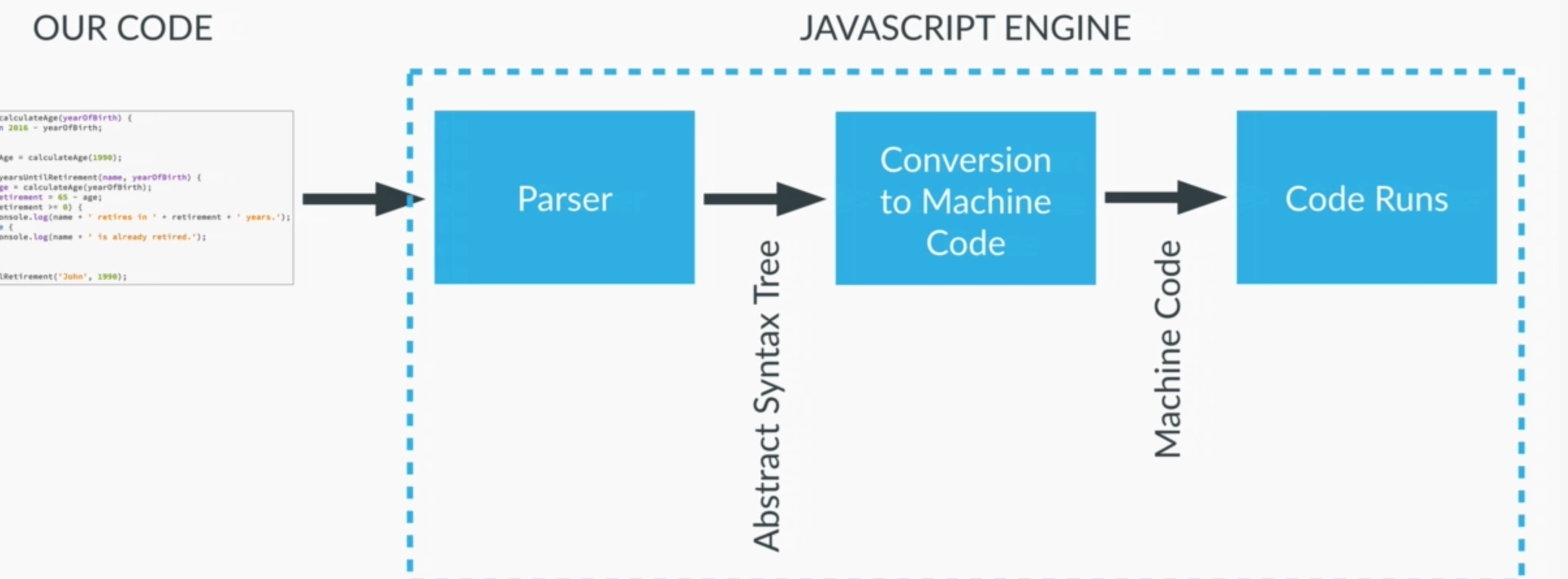
3. Data Types¶
console.log(typeof a)¶
var a = Infinity, NaN, 0, -1, 1.1, - `number`
var a = undefined - `undefined`
var a = Null , {}, {a:'a', b:1}, [1,2,3] - `Object`
var a = "1" , '1' - `string`
var a = true -- `boolean`
var a = function() {} - `function`
null vs Undefined¶
- Both have internally same value. hence
if(null == undefined) : true. - Both have diff type as shown above. hence
if(null === undefined) : false. var a = undefined: technically assign it but no purpose.
3. NaN¶
- its a error return by JS while mathematical error on number types.
- NaN is of number type.
- technically we can say its undefined number in JS world.
function type¶
- functional declaration vs
- function call vs
- function assign (fn expression) vs
- regular function vs
- arrow function (short hand, but lexical this)
var a = function calc(var1, var2){ return var1 + var2; }; console.log( typeof a); //"function" console.log( a(2,3)); // 5 console.log( calc(2,3)); //"ReferenceError: calc is not defined
boolean¶
-
Number as boolean : false internally represents zero value, And true internally represent non-zero number.
if(0 == false){ console.log( 'true');} ;//true if(1 == true){ console.log( 'true');} ;//true if(-1 == true){ console.log( 'true');}; //true if(100 == true){ console.log( 'true');} ;//true if(1 == '1') - true if(1 === '1') - false -
string === true.
if("abc") console.log( 'true'); //output else console.log( 'false'); -
NULL == false
if(null) console.log( 'true'); else console.log( 'false'); //output