Fundamentals
A. Architecture¶
1. Change detection.¶
- https://chat.deepseek.com/a/chat/s/f3b93971-68b6-4204-b9c1-7380c3164ffd
- changeDetection: ChangeDetectionStrategy.OnPush /Default
- constructor(private cd: ChangeDetectorRef)
- TrackBy Function |
B. Developer¶
1. NgModules¶
- it provides context for components
- An Angular app is defined by a set of NgModules
- one root module (which provides the bootstrap mechanism that launches the application)
- many feature modules.
- benefits
- Organizing complex applications into distinct functional modules
- helps in managing development, designing, re-usability, scalibity, etc
- Also lazy-loading of module. :pont_left:
- import/export
- NgModules can import functionality from other NgModules
- and allow their own functionality to be exported and used by other NgModules
- root module (bootstrap, special module)
- Could lazily load feature modules via ng routing
- it will load registered comp + child comp
2. Components¶
- purpose: moudule design, resuabilty, etc - Each component defines:@Component({ selector: 'app-signin', templateUrl: './signin.component.html', styleUrls: ['./signin.component.css'] }) selector: 'app-signin' | <div app-signin> </div> selector: '[app-signin]' | <div app-signin> </div> selector: '.app-signin' | <div class="app-signin"> </div>2.1 component TS¶
- @Component class component-1
- has application data and logic
- constructor()
- @Injectable service-1 : to load backend data
- service-1
- service-2
- ...
2.2 view¶
- HTML, that defines a view. has:
- html5-tags
- ng-component-selector
- ng-directive-selector
- ng-pipe
- ...
- inline:
templateor external:templateUrl - Template Expressions --> The text inside {{ }}
- Template Statement --> (event) = statement
2.3 styling¶
styleUrls,styles- many css/scss files
- npm install bootstrap@3y
- go tp angular.json > add : "style": [ "node_module/bootstrap/dist/css/bootstrap.min.css" **, "src/styles.css"]
- global styling - ../src/styles.css
2.4 more¶
providers- optional, to inject Services to component and to its child component.animation- optional. 011_Animation.mdselector: custom tag for componentencapsulation:- native : same as Emulated, but won't work in older browser
- None :
- ng will not unique property/attribute
- hence parent component style will be applied.
- Emulated
- ng adds unique property in every element. eg : ng-content-ego-2
- then later it is used by css property selector to apply style.
2.5 Component Communication Scenarios¶
- check sample code: 100_project_1_Component_Comm.md
- scenario-1/2 :: parent->child | parent<-child comm
parent-component-1child-component-1(EventEmitter-1, subject-1)
- scenario-3 : sibling comp comm
service-1(EventEmitter-1, subject-1), inject to both comp:comp-1comp-2
NEXT - @ViewChild: Accessing a specific element or component - @ViewChildren: Accessing multiple elements/components of the same type - @ContentChild: Accessing projected content (ng-content) - @ContentChildren: Accessing multiple projected components - https://chat.deepseek.com/a/chat/s/5f94f633-26f3-4d75-bbda-f085f8965e0f
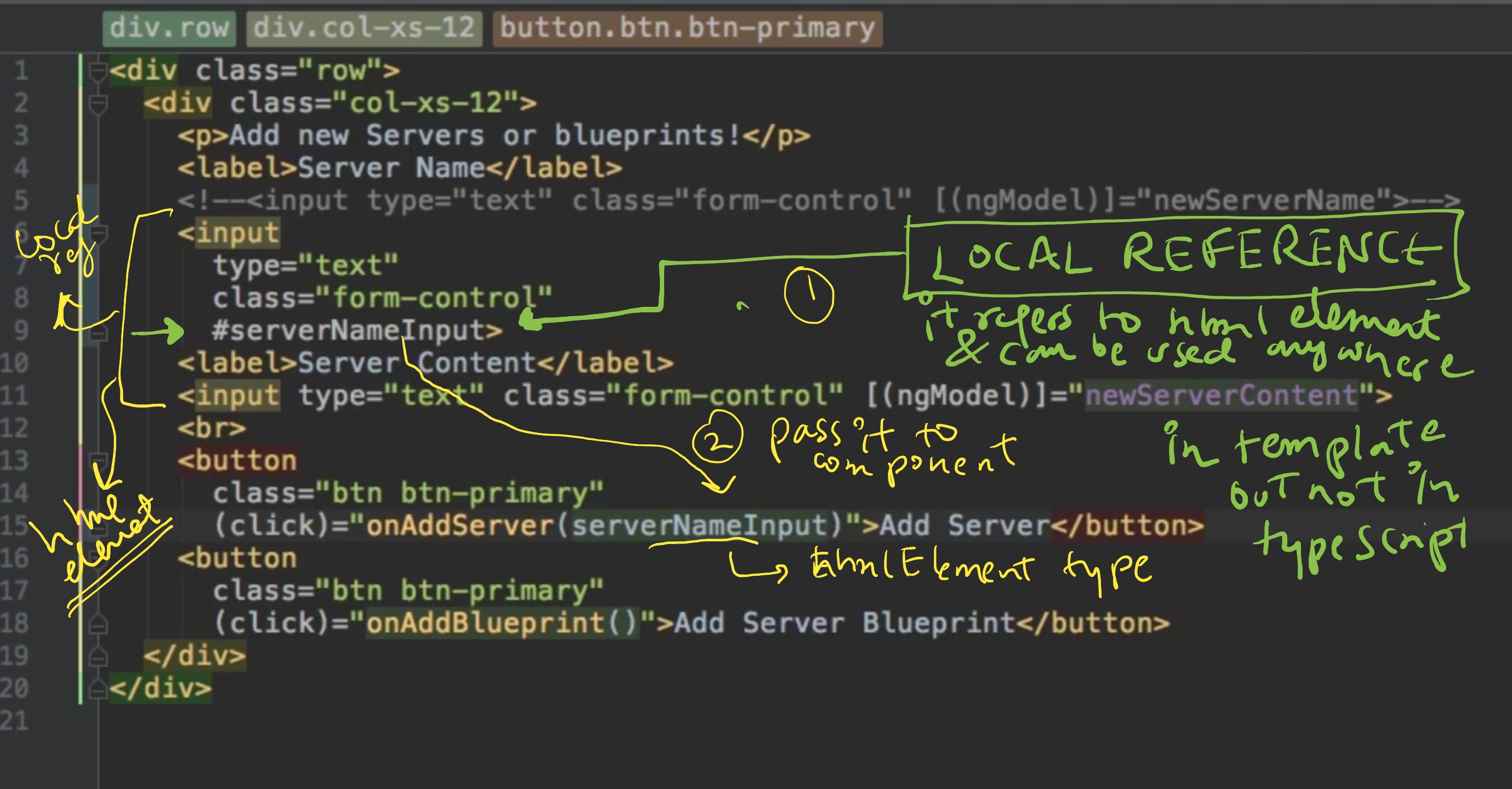
2.6 local-reference and @viewChild @viewChildren
¶
- Inside view, Create references on any html-element / component. eg
#ref1 - using local reference:
- way-1 (old tricky): pass js-object (eg: HTMLInputElement) while calling method.
<input> (change)=m1(ref1: HTMLInputElement) </input> - way-2 (use this, preferred ): @viewChild / @viewChildren
- life cycle hook :: ngAfterViewInit() { }
--- template / view --- <h1 #ref1 >Angular View Decorators Demo</h1> <comp-1></comp-1> <comp-2 [name]="'First Item'" #ref2> </comp-2> <comp-2 [name]="'Second Item'" #ref3> </comp-2> --- comp TS --- // Class Component-2 :: selector - comp-2 // Class Component-2 :: selector - comp-2 @ViewChild('ref1') viewElement: ElementRef; @ViewChild(Component-1) viewElement: Component-1; // Class Component-1 :: selector - comp-1 @ViewChildren('ref2, ref3') viewElements: QueryList<ElementRef>; @ViewChildren('ref1, ref2, ref3') viewElements: QueryList<ElementRef>; @ViewChildren(Component-2) viewElements: QueryList<Component-2>; === Life cycle === ngAfterViewInit() { // refer these - viewElement + viewElements }
- life cycle hook :: ngAfterViewInit() { }
2.7 content projection and @ContentChild @ContentChildren
¶
- ng-content directive
- life cycle hook :: ngAfterContentInit() {}
- understand by example
template (Component-2 :: selector - comp-2): <h3>Box Component</h3> <ng-content></ng-content> << catch PROJECTED content here >> <div>Projected content ends here</div> Component-2 TS @ContentChild('ref1') projectedParagraph: ElementRef; @ContentChild('ref2') firstProjectedItem: Component-2; @ContentChildren(Component-1) projectedItems: QueryList<Component-1>; lifeCycle: ngAfterContentInit() { // projectedParagraph, firstProjectedItem, projectedItems } app-component (root module) html/view <comp-2> // project here with local reference - ref1, ref2 // <comp-1> </comp-1> //Component-1 </comp-2>
2.8 LifeCycle :yellow_circle:¶
- https://angular.dev/guide/components/lifecycle
- https://chat.deepseek.com/a/chat/s/6cbd1509-8d5d-4564-93e2-5017ffe902b9
Creation Phase: Constructor → ngOnChanges → ngOnInit → ngDoCheck → [ ngAfterContentInit → ngAfterContentChecked ] → [ ngAfterViewInit → ngAfterViewChecked ] Update Phase: ngOnChanges → ngDoCheck → ngAfterContentChecked → ngAfterViewChecked Destruction Phase: ngOnDestroy
Hook Timing Purpose Frequency Notes Constructor Before any other lifecycle hook Dependency injection, simple initializations Once Not technically a lifecycle hook ngOnChanges()Before ngOnInit()and when input properties changeRespond to input changes Before init and when inputs change Receives SimpleChangesobjectngOnInit()After first ngOnChanges()Component initialization Once Preferred place for complex initializations ngDoCheck()During every change detection run Custom change detection Very frequent Use carefully for performance ngAfterContentInit()After content projected Respond to content projection Once After first ngDoCheck()ngAfterContentChecked()After projected content checked Respond after content check After every ngDoCheck()Runs frequently ngAfterViewInit()After component's view initialized Access view children Once Safe to access child components ngAfterViewChecked()After view checked Respond after view check After every ngAfterContentChecked()Runs frequently ngOnDestroy()Before component destruction Cleanup Once Unsubscribe, clear timers here - Best Practices
✅ Do: - Use
ngOnInitfor initialization - Clean up inngOnDestroy- UsengAfterViewInitto access view children - Be cautious with frequent hooks (ngDoCheck,ngAfter*Checked)❌ Don't: - Put complex logic in constructor - Forget to unsubscribe from observables - Modify views in change detection hooks (can cause errors)
3. Directives¶
4. Binding/s¶
- https://chat.deepseek.com/a/chat/s/6cbd1509-8d5d-4564-93e2-5017ffe902b9
4.1 String Interpolation - {{ }}¶
<p>{{ title }}</p> <p>1 + 1 = {{ 1 + 1 }}</p> <p>Hello, {{ getUserName() }}</p> --- {{fn(msg)}} Anything which get converted into string is ok. --- <p> {{ var1 }} </p> | <p [innerText]=var1 > </p> // trick-1 : both are same4.2 Event binding (View >> Component)¶
$eventis reserved keyword to capture the event data.- case-1: html event binding
<button (click)="onButtonClick()">Click me</button> <input (keyup)="onKeyUp($event)"> -
(< HTMLInputElement >e.target).value
-
case-2: custom ng-event
- @output event-1: EventEmitter < string >
- @output event-2: Subject < T >
<comp-1 (event-2)="onEvent2($event)">
4.3 Property binding (Component >> View)¶
- attribute of html tag
- property of ng-comp/ng-directive
- examples
<html-tag-1 [attribute]="var-1" /> <comp1 [property-1]="'string-value'" > === property="string-value" <comp1 [ng-directive1]=value /> <comp1 [property-1]=value /><img [src]="imageUrl" [alt]="imageAlt"> <button [disabled]="isDisabled">Click me</button> <div [class.active]="isActive"></div> <div [style.color]="textColor"></div>--- view --- <button [disabled]="'true'"> </button> //static <button [disabled]="'false'"> </button> //static <button [disabled]="newValue"> </button> //dynamic --- component --- boolean newValue = true; setTimeOut( () => newvalue != newvalue, 5000); //after 5 sec toggle.
4.4 two-way data binding¶
- custom-1 - create var var1 - create m1(event){...} - in html : [attribute-1]=var1 - in html : (click) = m1($event) - custom-2<input [(ngModel)]="userName"> <!-- Equivalent to: --> <input [ngModel]="userName" (ngModelChange)="userName = $event"> //remember to import **FormsModule** in your app module for **ngModel**@Input() value: any; @Output() valueChange = new EventEmitter<any>(); <app-custom [(value)]="someValue"></app-custom>4.5 more on binding¶
=== Attribute Binding === <button [attr.aria-label]="closeLabel">X</button> <td [attr.colspan]="colSpan"></td> === Class Binding === <div [class.special]="isSpecial"></div> <div [class]="classExpression"></div> <!-- replaces all classes --> === Style Binding === <button [style.color]="isSpecial ? 'red' : 'green'">Button</button> <div [style.width.px]="widthValue"></div> === special binding === === *ngFor (Structural directive) === <ul> <li *ngFor="let item of items; let i = index"> {{ i }} - {{ item.name }} </li> </ul> === *ngIf (Structural directive) === <div *ngIf="showElement; else otherTemplate"> Content to show when condition is true </div> <ng-template #otherTemplate> Alternative content </ng-template> === ngSwitch === <div [ngSwitch]="value"> <p *ngSwitchCase="'A'">Value is A</p> <p *ngSwitchCase="'B'">Value is B</p> <p *ngSwitchDefault>Value is something else</p> </div>
5. Pipes¶
010_Pipes.md - transforming values, eg; dates and currency - Angular provides predefined pipes for common transformations, - define custom pipes.
6. Services¶
- Purpose
- Act as end point to interact with backend/server
- Components interaction.
- Class with decorator @Injectable()
- injection
- Declare services in NgModule provider section.
- registers service with NgModule
- Add it in export section to make services avialable to other module.
- module is loaded, loads registered services along with it, lazily.
- register
- Declare services in Component provider section.
- it will inject the service into component
- and its child comp.
- so, if we define Service at app Module, it will avilable to all inner module of app, no import is required.
- ng g s Myservice1 - ng generate service Myservice1
7. Routes¶
- Router service helps in define navigation paths among Angular-views (template + Component)
- It maps URL-paths to Angular-views, instead of traditional JSP pages.
- Follows browser convention : URL in the address bar, Click links and browser's back &forward buttons.
- Apart from that we can navigate to new views when the user clicks a button or selects from a drop box.
- router can lazy-load the module
- router logs activity in the browser's history
- The router interprets a link URL according to your app's view navigation rules and data state. and shows or hides view hierarchies.
8. Forms¶
- Declarative
- Reactive
9. testing :¶
- jasmine
- Karma
10. lib¶
- Rxjs : Observables
- Angular itself used it alot.
- Alternative for promise.
- new :
signal - HttpClient
- New:
HttpClientModule(added in ng6) - 009_HTTP_1.md
- 009_HTTP_2.md
- 009_HTTP_3_CP.md
- 009_HTTP_CLIENT_1.md
- 009_HTTP_CLIENT_2.md
- NgRx
- State management in Angular
- 012_NgRX_1.md
- 012_NgRX_2_PRG-1.md
- 012_NgRX_2_PRG-2.md